Social Justice in the 21st Century: Meaning, Challenges, and the Path Forward
IntroductionSocial justice is one of the most powerful and enduring ideals that shapes modern societies. It represents the belief that every individual deserves equal rights, opportunities, dignity, and access to basic resources, regardless of their caste, class, gender, race, religion, or economic background. In the 21st century—an era marked by rapid technological advancement, economic globalisation, and rising inequalities—the demand for social justice has become even more urgent. Movements worldwide, from the fight against racial discrimination to campaigns for gender equality, labour rights, and digital inclusion, highlight an essential truth: a society cannot progress unless all its members progress equally. This essay explores the meaning of social justice, its historical evolution, its key dimensions, the challenges faced today, and the way forward.
________________________________________ Meaning and Core Principles of Social Justice
Social justice is built on a foundation of fairness and equality. It involves not just ensuring legal rights, but also guaranteeing that social, economic, and political systems work equitably for all individuals. The core principles include:
• Equality: Equal access to rights, resources, and opportunities.
• Equity: Fair distribution based on individual needs and circumstances.
• Rights: Protection of civil, political, social, and economic rights of all.
• Participation: Ensuring every individual can take part in decision-making processes.
• Human Dignity: Recognizing the inherent worth of every human being.
Together, these principles form a framework that aims to correct historical injustices and prevent new forms of discrimination or exclusion.
________________________________________ Historical Background
Social justice has roots in ancient philosophy, religious texts, and political thought.
• Ancient Indian philosophies, such as Buddhism and teachings of the Bhakti and Sufi saints, emphasized compassion, equality, and non-discrimination.
• European Enlightenment thinkers, including Rousseau and Locke, stressed natural rights and equality.
• The Industrial Revolution heightened economic inequalities, giving rise to worker movements, trade unions, and the modern concept of social justice tied to labour rights.
• After World War II, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) established global norms for equality and dignity.
• In India, the Constitution makers embedded social justice as a core value through the Preamble, Fundamental Rights, and Directive Principles of State Policy.
Thus, the idea of social justice is not new but has evolved constantly to meet the needs of changing societies.
________________________________________ Key Dimensions of Social Justice
Social justice covers multiple interconnected areas:
1. Economic Justice
It aims to reduce economic inequality and ensure fair distribution of wealth, income, and opportunities. Access to employment, fair wages, social security, and financial inclusion are essential elements.
2. Social Justice
This includes eradicating discrimination based on caste, gender, religion, ethnicity, race, or disability. It demands respect for diversity and inclusion in all spheres of life.
3. Political Justice
It ensures equal participation in democratic processes, representation in decision-making bodies, and protection of civil liberties like freedom of speech, expression, and association.
4. Gender Justice
Gender justice focuses on creating an equitable world for all genders by eliminating patriarchy, gender-based violence, wage gaps, and stereotypes.
5. Digital Justice
In the digital era, social justice includes equal access to technology, digital literacy, privacy protection, and fairness in artificial intelligence and online platforms.
________________________________________ Contemporary Challenges to Social Justice
Despite constitutional frameworks and policy efforts, several challenges continue to hinder social justice:
1. Economic Inequality
The gap between the rich and poor has widened. While a small percentage of the population accumulates wealth, millions lack access to basic services like healthcare, education, and housing.
2. Caste-Based Discrimination
In India, caste continues to influence social status, access to resources, and opportunities. Untouchability persists in subtle and overt ways.
3. Gender Inequality
Women and gender minorities face violence, unequal pay, low representation in politics and corporate leadership, and social restrictions.
4. Racial and Ethnic Discrimination
Globally, racism remains a significant barrier to social justice. Migrants, refugees, and minority groups often face systemic biases.
5. Digital Divide
The lack of access to internet services and devices excludes millions from education, employment, and governance benefits.
6. Climate Inequality
Climate change affects vulnerable communities the most, creating environmental injustice.
7. Inequitable Healthcare Access
COVID-19 highlighted severe disparities in access to medical facilities, vaccines, nutrition, and sanitation.
________________________________________ Role of the Constitution and Government Policies
In India, social justice is deeply embedded in the constitutional framework.
• Fundamental Rights protect equality, freedom, and justice for all.
• Directive Principles guide the state to promote education, health, livelihood, and welfare.
• Policies such as MGNREGA, Right to Education, reservation system, Ayushman Bharat, PM-KISAN, and Digital India aim to correct socio-economic imbalances.
• Laws like the SC/ST Prevention of Atrocities Act, Right to Information Act, Food Security Act, and POSH Act strengthen social justice.
While progress has been made, effective implementation remains crucial.
________________________________________ Role of Civil Society and Social Movements
Civil society plays a vital role in strengthening social justice:
• Women's movements have fought for gender equality and reproductive rights.
• Tribal and Dalit movements have challenged discrimination and demanded dignity.
• Environmental groups advocate for sustainable development.
• Student movements demand affordable education.
• International movements like Black Lives Matter highlight global injustice.
These movements shape public consciousness and hold institutions accountable.
________________________________________ The Path Forward
Achieving social justice requires coordinated efforts at multiple levels. Key steps include:
• Ensuring inclusive and equitable education.
• Generating dignified employment and fair wages.
• Reducing caste and gender discrimination through awareness and strict enforcement.
• Expanding social security for vulnerable populations.
• Bridging the digital divide.
• Ensuring environmental sustainability and climate justice.
• Promoting representation of marginalized groups in policymaking.
• Strengthening legal frameworks and accountability mechanisms.
• Leveraging technology ethically to serve the poor, not exploit them.
Most importantly, social justice needs a cultural shift—towards compassion, tolerance, and collective responsibility.
Conclusion
Social justice is not just a policy goal—it is a moral commitment that defines the soul of a society. A nation’s progress is meaningful only when the most marginalized feel empowered and included. In today’s rapidly changing world, the fight for social justice is more relevant than ever. Whether it is economic inequality, digital exclusion, gender discrimination, or racial injustice, societies must work collectively to build systems that are fair, inclusive, and humane. True social justice is achieved when every person has the opportunity to live with dignity, freedom, and hope.
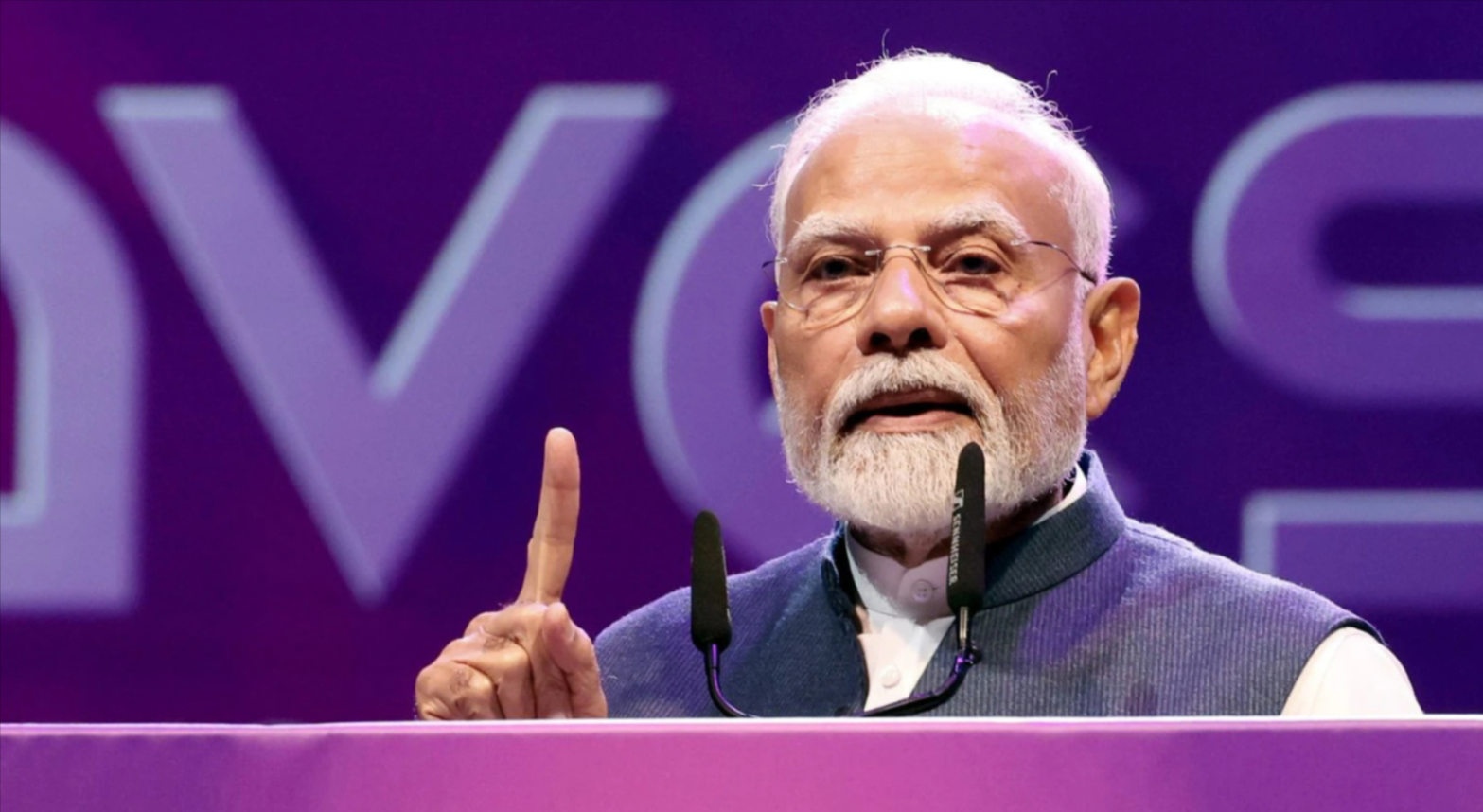
During the WAVES Summit in Mumbai, Prime Minister Narendra Modi underlined India's developing position in the global creative economic sector. During his opening address, India earned the description of an "orange economy" because cultural and creative sectors drive both financial growth and job creation. Rajnikanth and Mukesh Ambani joined
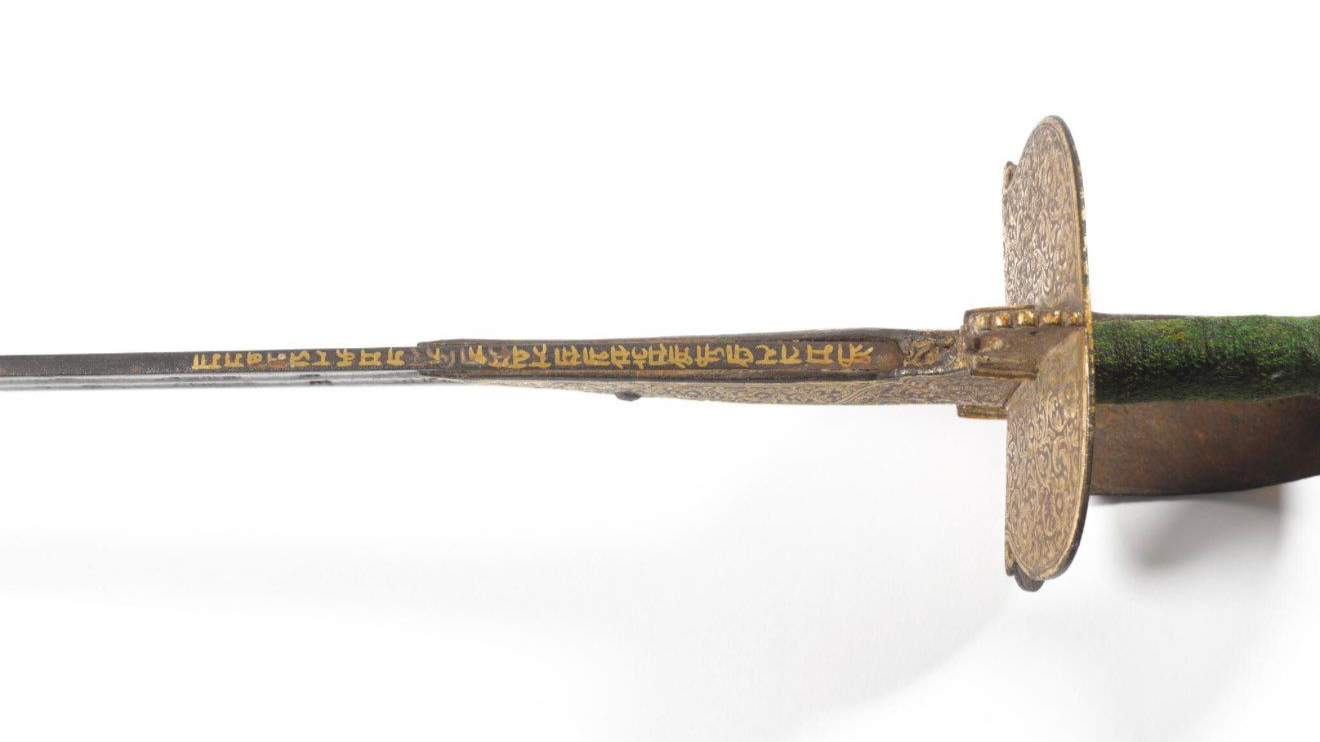
The Mahahtra government achieved a historical milestone by returning to India the historic sword of Raghuji Bhosale I during a Sotheby’s auction in London, which belonged to a notable 18th-century Maratha ruler. The state of Mahahtra achieves its first success in acquiring historical artifacts from international auctions. The bidding

Stay updated with The Hindu Editorial Vocab24 app, your definitive source for breaking news and comprehensive coverage from India and around the globe. Whether it's political developments, business updates, sports highlights, the latest technology trends, or current events, The Hindu brings live, accurate, and reliable news directly to your device.
Don’t fall for sensationalized or fake news shared online. Read and share accurate updates with friends and family through The Hindu Editorial Vocab24 app. Download it today!
News Coverage in The Hindu Editorial Vocab24 App
Breaking News: Receive instant notifications on breaking news stories as they unfold. Stay informed about major events and developments in India and around the world with live blogs, news in shorts videos, and concise articles.
Politics: Get the latest updates on Indian politics, including elections, policy changes, government decisions, and political events that shape the nation.
Business and Economy: Stay ahead in the economic landscape with detailed business news and market analysis. Learn about stock market trends, financial reports, corporate news, and economic developments to make informed investment decisions.
Current Events: Follow stories on social issues, policy changes, global events, and daily current affairs, tailored for UPSC and other competitive exam preparations.
Technology: Keep up with the latest gadgets, innovations, and tech trends. Read expert reviews and analyses in short, concise updates on cutting-edge technology from India and beyond.
Sports: Never miss a moment of your favorite sports. Get live scores, match reports, and expert analysis on cricket, football, tennis, and more.
International News: Stay informed about global events and geopolitical developments, including the Russia-Ukraine war, Israel-Palestine conflict, and other key international stories.
Local News: Stay connected to your community with the latest updates on city events, issues, and local news. Coverage includes hyperlocal updates from cities like Bangalore, Chennai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Kolkata, and more.
Trending Topics: Discover what's trending today with the most talked-about stories and hot topics across India and the world.
Experience journalism that values integrity, accuracy, and reliability. Download The Hindu Editorial Vocab24 app today and stay connected with the world.
Subscribe to our newsletter!